How to Batch Similar Tasks for Peak Efficiency presents a vital approach to maximizing productivity in our fast-paced lives. By grouping similar tasks together, individuals and organizations can streamline their workflows and enhance focus. This method not only saves time but also minimizes the mental fatigue associated with constantly switching tasks.
The practice of batch tasking allows for a structured method of tackling daily responsibilities, resulting in heightened efficiency. Understanding its psychological benefits and dispelling common misconceptions can encourage more people to adopt this effective time management strategy. In this discourse, we will explore how identifying similar tasks, designing a batch schedule, and utilizing appropriate tools can lead to significant improvements in personal and professional productivity.
Understanding Batch Tasking
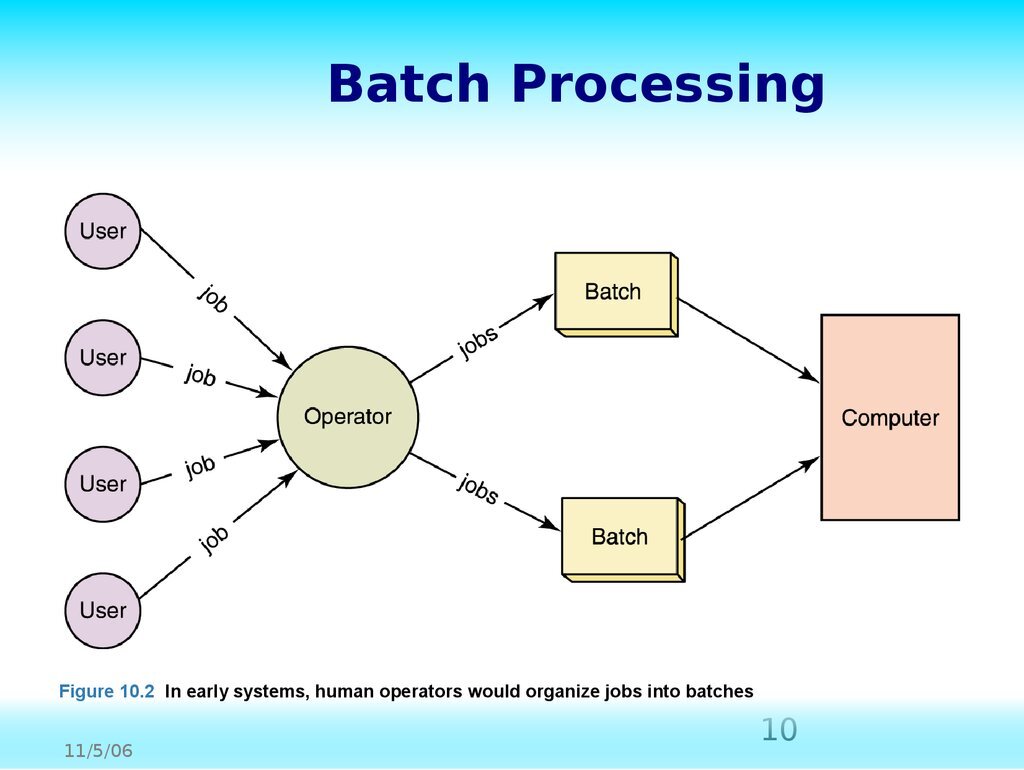
Batch tasking is a time management technique that involves grouping similar tasks together and performing them consecutively without interruption. This method is essential for enhancing productivity, reducing mental fatigue, and increasing overall efficiency. By concentrating on one type of task at a time, individuals can minimize the cognitive load associated with task switching and create a more streamlined workflow.The psychological benefits of batch tasking are significant.
When tasks are performed in clusters, individuals experience a sense of accomplishment as they complete batches rather than switching between various types of work. This focused approach can lead to a boost in motivation and a reduction in feelings of overwhelm. Moreover, batch tasking fosters a clearer mindset, as the individual can immerse themselves in specific activities, ultimately resulting in higher quality outputs.
Common Misconceptions about Batch Tasking
Despite its advantages, several misconceptions surround batch tasking that may deter individuals from adopting this practice. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for embracing batch tasking effectively.
- Batch tasking is only for large projects: Many believe that batch tasking is only beneficial for extensive, long-term projects. In reality, it can be applied to daily tasks such as responding to emails or making phone calls, regardless of their size.
- It limits flexibility: Some think that batching tasks restricts their ability to adapt to new priorities. However, batch tasking can include designated time blocks that allow for adjustments while maintaining focus.
- It requires more time to set up: There is a perception that organizing tasks into batches takes more time upfront. In fact, this initial investment can save significant time in the long run by reducing the inefficiencies associated with multitasking.
“Batch tasking can transform your approach to productivity, making it more efficient and less stressful.”
Identifying Similar Tasks
To effectively batch tasks for peak efficiency, it is crucial to identify which tasks can be categorized as similar. By recognizing these similarities, individuals can streamline their workflow and reduce the time spent transitioning between different types of activities. This section details the criteria for categorizing tasks, provides examples of tasks that can be grouped together, and Artikels methods for assessing task similarity and potential efficiency gains.
Criteria for Categorizing Tasks
Establishing clear criteria for categorizing tasks as similar is essential for effective batching. Here are some key criteria to consider when identifying similar tasks:
- Nature of the Task: Tasks that require the same skills or resources can often be grouped together. For example, all writing tasks, whether they involve drafting emails, reports, or articles, can be categorized as similar.
- Duration: Tasks that take approximately the same amount of time to complete can be batched. For instance, if a series of tasks each take around 15 minutes, they can be grouped together to maximize efficiency.
- Location: Tasks that can be performed in the same physical or digital space are often similar. For example, all tasks that require access to specific software or tools should be completed in one session.
- Goal or Outcome: Tasks aiming for similar outcomes can be batched. For example, all customer service responses addressing similar inquiries can be grouped to ensure uniformity in communication.
Examples of Grouped Tasks for Batching
When identifying tasks to batch, it can be helpful to consider specific examples. The following lists illustrate tasks that can be effectively grouped together:
- Administrative Tasks: Scheduling meetings, filing paperwork, and organizing digital files can all be completed in a single session to minimize distractions.
- Communication Tasks: Answering emails, making phone calls, and responding to messages can be efficiently handled together, allowing for focused communication time.
- Research Tasks: Gathering data, reviewing articles, and compiling notes can be performed sequentially, maintaining a consistent flow of information.
- Creative Tasks: Brainstorming ideas, drafting content, and designing visuals can be effectively batched to enhance creativity and maintain momentum.
Methods for Assessing Task Similarity and Efficiency Potential
To assess task similarity and evaluate the potential for increased efficiency through batching, several methods can be employed:
- Time Tracking: Keeping a record of how long each type of task takes can reveal patterns that indicate which tasks are best suited for batching.
- Task Analysis: Reviewing past completed tasks and their outcomes can help identify which tasks naturally align with one another, thus allowing for better grouping.
- Feedback Gathering: Engaging with team members or colleagues about their experiences with specific tasks can provide insights into which activities they perceive as similar.
- Trial and Error: Experimenting with various batch configurations and observing the results can help determine the most effective combinations of tasks for improved efficiency.
“Batching similar tasks can significantly reduce the cognitive load and transition time, leading to enhanced productivity.”
Designing a Batch Schedule
Creating an effective batch schedule is pivotal for optimizing productivity and ensuring that similar tasks are completed efficiently. A well-structured schedule not only enhances focus but also minimizes the time lost in transition between different types of tasks. Below are essential steps and techniques that assist in designing a robust batch schedule.
Creating an Effective Schedule for Batch Tasking
To create a schedule that maximizes efficiency, it is crucial to allocate specific time blocks dedicated to each category of task. This involves identifying the tasks that can be grouped based on their nature, complexity, and required resources. A typical batch schedule can be structured as follows:
- Identify Task Groups: Categorize tasks based on similarities, such as administrative duties, creative work, or meetings.
- Allocate Time Blocks: Assign specific time slots for each category, ensuring that they align with peak productivity periods. For example, creative tasks may be best suited for morning hours when mental energy is high.
- Set Duration for Each Block: Define how long each batch will last. Research suggests that 90-minute focused sessions followed by short breaks can significantly boost concentration and output.
“The key to productivity is not just time management, but energy management.”
Techniques for Allocating Time Blocks
Employing effective techniques for allocating time blocks can enhance the efficacy of batch tasking. Here are some useful methods:
- Time Blocking: Assign specific blocks in your calendar for different task categories. This method helps to prevent multitasking and allows for deeper focus.
- Prioritization: Use tools like the Eisenhower Matrix to determine which tasks to batch together based on their urgency and importance.
- Consistent Scheduling: Try to keep the same time slots for similar tasks each week. This consistency helps in forming a habit and streamlining your workflow.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your time blocks and adjust them based on performance metrics or changing priorities.
Importance of Flexibility in a Batch Schedule
Flexibility is a fundamental aspect of any batch schedule, as it allows for adjustments based on unforeseen circumstances or shifting priorities. While structure is essential, being adaptable can lead to better stress management and increased satisfaction in task completion. Maintaining flexibility involves:
- Buffer Times: Incorporate buffer times between task blocks to account for overruns or unexpected interruptions.
- Weekly Reviews: At the end of each week, evaluate what worked and what didn’t, and be willing to modify your schedule accordingly.
- Open to Change: Embrace the notion that plans may change, and be prepared to reorganize your schedule to accommodate critical tasks.
A successful batch schedule is one that can be both structured and adjustable, allowing individuals to work efficiently while also managing the inevitable changes in workload and priority.
Tools and Techniques for Batch Tasking
Batch tasking can significantly enhance productivity by organizing similar tasks into cohesive groups, enabling efficiency and focus. Utilizing the right tools and techniques becomes essential for successfully implementing this strategy. A variety of software applications and organizational techniques exist, each tailored to support the batching process by automating and streamlining task management.
Software and Tools that Facilitate Batch Tasking
Several tools can effectively aid in batch tasking, making it easier to manage workload and maintain focus. Below are notable software options that provide features conducive to organizing similar tasks:
- Trello: This flexible project management tool allows users to create boards for different projects and add cards for specific tasks, which can be grouped by type for efficient batch processing.
- Asana: Asana helps organize tasks and projects into lists and boards, making it easy to categorize and batch similar tasks effectively.
- Todoist: A task management app that allows users to create projects and sub-tasks, enabling straightforward batch organization.
- Microsoft To Do: This application assists in creating tasks and lists, ideal for grouping similar activities and tracking their completion.
- Notion: A versatile workspace that combines notes, tasks, databases, and calendars, allowing customized structures for batch task management.
Step-by-Step Guide on Using Trello for Organizing Tasks
Trello is a popular tool for batch tasking due to its visual layout and flexibility. Here is a step-by-step guide to utilizing Trello for organizing tasks:
- Create a Trello Account: Sign up for a free Trello account if you do not have one.
- Set Up a Board: Create a new board specific to your project or task theme.
- Add Lists: Create lists for different categories of tasks, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Completed.”
- Create Cards: For each task, create a card within the relevant list. Include detailed descriptions, deadlines, and checklists as necessary.
- Group Similar Tasks: Move cards into the same list based on their nature or type to streamline your focus on similar activities.
- Utilize Labels: Use color-coded labels to signify priority levels or categories, facilitating quick identification of tasks.
- Assign Due Dates: Add deadlines to tasks to ensure timely completion and maintain productivity.
- Track Progress: Move cards between lists as you progress through tasks, visually indicating status changes.
Methods for Tracking Progress and Adjusting Batches
Tracking progress is crucial for evaluating batch tasking effectiveness. Various methods can be employed to ensure continuous improvement:
- Daily or Weekly Reviews: Set aside time regularly to review completed tasks and assess what worked well and what could be improved in future batches.
- Time Tracking Tools: Utilize applications such as Toggl or Clockify to monitor the time spent on each task or batch, allowing for better planning in subsequent sessions.
- Adjusting Batches: If certain tasks take longer than expected or disrupt flow, consider splitting larger batches into smaller, more manageable segments to maintain focus and productivity.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement a system for gathering feedback on task efficiency from team members (if applicable) to refine batching strategies.
Implementing Batch Tasking in Daily Life
Incorporating batch tasking into daily routines can significantly enhance productivity and reduce the cognitive load associated with multitasking. By efficiently grouping similar tasks, individuals can streamline their workflows, allowing for greater focus and improved time management. This section will Artikel strategies for integrating batch tasking into everyday life, address common challenges encountered during the initial stages, and provide methods for assessing the effectiveness of this approach.
Strategies for Incorporating Batch Tasking
To effectively implement batch tasking, consider the following strategies that can be seamlessly integrated into daily routines:
- Identify and categorize tasks: Begin by listing all daily activities and categorizing them into similar groups, such as administrative tasks, creative work, or communication duties. This foundational step will clarify which tasks can be batched together.
- Set specific times for batch sessions: Designate specific blocks of time each day or week dedicated solely to completing batch tasks. For example, reserve mornings for emails and administrative work, while afternoons can focus on project development.
- Limit distractions: During batch task sessions, create an environment conducive to focus. This may involve silencing notifications, utilizing noise-canceling headphones, or working in a distraction-free space.
Overcoming Common Obstacles
Beginning the practice of batch tasking may present various challenges, but these can be effectively navigated with the right strategies:
- Resistance to change: Many individuals are accustomed to traditional task management methods. To overcome this, start by implementing batch tasking with a single type of task, gradually expanding as comfort grows.
- Difficulty in identifying similar tasks: To address this, maintain a running list of tasks completed each day. Review it weekly to identify patterns and opportunities for batching tasks together more effectively.
- Time management concerns: Initially, batch tasking may seem time-consuming. However, tracking time spent on individual tasks will reveal potential efficiencies, reinforcing the value of this approach.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Batch Tasking
To gauge the success of batch tasking in enhancing personal workflows, consider implementing the following evaluation methods:
- Track performance metrics: Monitor task completion rates before and after adopting batch tasking. This data will provide insight into improvements in efficiency and productivity.
- Solicit feedback: Regularly seek feedback from colleagues or supervisors regarding the quality and timeliness of work completed during batch task sessions. This external perspective can highlight areas of improvement.
- Reflect on personal satisfaction: Keep a journal documenting experiences with batch tasking, noting feelings of accomplishment and stress levels. This subjective measure can inform adjustments to the batching process.
“Batch tasking not only enhances productivity but also fosters a greater sense of control over one’s workday.”
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Batch tasking has been effectively utilized by numerous individuals and organizations to enhance productivity and achieve peak efficiency. By grouping similar tasks, these entities have not only saved time but also improved focus and the quality of their work. This section explores notable case studies that exemplify the successful application of batch tasking and analyzes the varying approaches taken, along with the valuable lessons learned.
Individual Case Studies of Batch Tasking
A prime example of an individual successfully employing batch tasking is renowned author Tim Ferriss. His approach is prominently featured in his bestselling book, “The 4-Hour Workweek.” Ferriss schedules specific blocks of time for check-ins and communications, limiting his email responses to just two times per week. This strategy has allowed him to dedicate more time to writing and creative thinking, ultimately resulting in greater output and reduced distraction.
The key takeaway from Ferriss’s experience is the significant improvement in focus achieved by minimizing context-switching.
Organizational Case Studies of Batch Tasking
Organizations such as Google have also embraced batch tasking to optimize team productivity. For instance, Google implemented a “deep work” initiative where employees are encouraged to reserve uninterrupted time slots for focused tasks. As a result, teams that adopted this practice reported a 30% increase in project completion rates. The organization realized that by creating a culture that prioritizes batch tasking, they could promote higher levels of engagement and innovation among employees.
Comparative Approaches to Batch Tasking
Different approaches to batch tasking have yielded varied outcomes. For example, contrasting Tim Ferriss’s individual methodology with Google’s organizational strategy reveals distinct advantages and challenges:
- Tim Ferriss: Focus on personal productivity through self-imposed restrictions on task frequency.
- Google: Institutional change promoting collaborative efforts and shared uninterrupted work periods.
These cases highlight that while individual approaches can lead to significant personal gains, organizational strategies can foster a collaborative environment that enhances overall productivity.
Lessons Learned from Case Studies
Insights gained from these case studies underscore several key principles of effective batch tasking:
- Minimize Context Switching: Transitioning between different types of tasks can lead to inefficiencies. Establishing dedicated time for similar tasks allows for deeper focus.
- Set Clear Boundaries: Whether on an individual or organizational level, defining specific times for batch tasks can prevent distractions and promote accountability.
- Engage in Continuous Improvement: Regularly assessing the effectiveness of batch tasking strategies enables individuals and organizations to adapt and refine their approaches for better results.
The application of batch tasking in these case studies reveals not only its practical benefits but also the importance of adaptability and continuous evaluation in achieving peak efficiency.
Continuous Improvement and Adjustment
Continuous improvement and adjustment in batch tasking techniques are essential for maximizing efficiency and maintaining productivity over time. As workflows evolve and new tasks emerge, refining batch tasking methods ensures that individuals and organizations can adapt to changing demands and optimize their performance. This section will explore strategies for enhancing batch tasking, including methods for gathering feedback and a framework for periodic reassessment.
Strategies for Refining Batch Tasking Techniques
To effectively refine batch tasking methods, it is crucial to adopt a systematic approach. Here are several strategies that can be beneficial:
1. Establish Clear Metrics
Define specific performance indicators that measure the effectiveness of your batch tasks, such as time saved, error reduction, or task completion rates.
2. Regular Reviews
Set up a schedule for regular evaluations of batch tasking methods. These reviews can help identify areas for improvement and allow for timely adjustments.
3. Incorporate Feedback Loops
Create avenues for team members or personal reflections to share their experiences and suggestions regarding batch tasking practices. This feedback is invaluable for understanding the impact of your techniques.
4. Stay Updated on Best Practices
Keep abreast of new research and developments in efficiency tools and batch tasking strategies. This may involve attending workshops, webinars, or reading relevant literature.
5. Pilot New Techniques
Experiment with new approaches on a small scale before wide implementation. This reduces risks and allows for better understanding of their effectiveness.
Gathering Feedback on Batch Scheduling Effectiveness
Collecting feedback is vital for assessing the effectiveness of batch scheduling. To facilitate this process, consider implementing the following methods:
Surveys and Questionnaires
Distribute tools to team members to gather insights on their experiences with batch tasks. Questions can cover areas such as clarity of instructions, perceived efficiency, and challenges faced during task execution.
One-on-One Check-Ins
Schedule individual meetings to discuss batch tasking practices. This creates a safe space for honest feedback and can provide deeper insights into personal experiences.
Performance Metrics Analysis
Analyze the data gathered from key performance indicators established during the refinement phase. This quantitative approach helps in making informed decisions about any necessary changes.
Framework for Periodic Reassessment of Tasks
A structured framework for periodically reassessing tasks and their batching methods is essential for sustained efficiency. The following steps Artikel this framework:
1. Task Inventory
Maintain an updated list of all tasks regularly performed. This should include details such as frequency, time required, and complexity.
2. Categorization of Tasks
Organize tasks into categories based on similarities and workflow compatibility. This will assist in identifying potential batches.
3. Set Evaluation Timelines
Decide on specific intervals (e.g., quarterly, bi-annually) for reassessing tasks and batch methods, ensuring a systematic approach to improvement.
4. Develop Improvement Plans
Based on the evaluations, create actionable plans for tasks that require refinement or adjustment. These plans should Artikel necessary changes and expected outcomes.
5. Implementation and Follow-Up
After adjustments are made, monitor the impact of these changes on efficiency. Follow up with team members to gather insights and assess the effectiveness of the new batching methods.By integrating these strategies, organizations and individuals can continuously enhance their batch tasking techniques, ensuring that they remain flexible and effective in an ever-changing work environment.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, embracing the principles of batch tasking fosters a more organized, efficient, and productive environment. As we have seen through various strategies, real-life examples, and continuous improvement techniques, this method not only enhances individual productivity but also contributes to the overall success of teams and organizations. By regularly assessing and refining our batching methods, we can ensure sustained peak efficiency in our daily lives.