How to Delegate Tasks Effectively to Free Up Your Time is a vital skill in today’s fast-paced work environment. Mastering delegation not only enhances productivity but also allows individuals to focus on higher-priority tasks. Many professionals grapple with the concept of delegation, often hindered by psychological barriers and misconceptions that can impede their efficiency. Understanding how to overcome these challenges can transform the way work is approached, fostering a culture of collaboration and trust.
In exploring how to delegate effectively, we will delve into identifying which tasks can be delegated, selecting the right individuals, and ensuring clear communication throughout the process. By strategically engaging team members and supporting their growth, you not only empower them but also create a more productive workplace. This journey towards effective delegation is essential for anyone looking to optimize their time and resources.
Understanding Delegation

Delegation is a critical skill in effective time management that empowers leaders and team members alike to share responsibilities and enhance productivity. By allowing others to take on tasks, individuals can focus on higher-level goals and strategic initiatives that require their unique expertise. Understanding delegation involves grasping not only its practical applications but also the psychological dynamics at play.The concept of delegation fundamentally revolves around entrusting specific tasks or responsibilities to others.
This is essential for maximizing efficiency and time utilization in both personal and professional contexts. When tasks are effectively delegated, it enables team members to contribute their skills, fosters collaboration, and promotes a sense of ownership across the team. However, several psychological barriers often hinder effective delegation. Individuals may struggle with issues such as trust, perfectionism, or fear of losing control, which can impair their willingness to delegate effectively.
Psychological Barriers to Effective Delegation
Several psychological factors can obstruct the delegation process. Understanding these barriers is crucial for overcoming them and fostering a more productive environment. The following are common hindrances to effective delegation:
- Trust Issues: Many individuals hesitate to delegate because they doubt the abilities of their colleagues or subordinates. This lack of trust can stifle team dynamics and limit overall productivity.
- Fear of Losing Control: Some leaders worry that delegating tasks will result in a loss of oversight. This fear can lead to micromanagement, which counteracts the benefits of delegation.
- Perfectionism: Individuals who hold themselves to exceedingly high standards often find it challenging to trust others to meet those same expectations. This mindset can prevent them from assigning tasks effectively.
- Insecurity: A lack of confidence in one’s own leadership abilities can lead to reluctance in delegating, as individuals may feel that taking on too much responsibility is a reflection of their competence.
Common Misconceptions About Delegation
Misunderstandings about delegation can lead to ineffective practices and a reluctance to engage in the process. Addressing these misconceptions is vital for fostering a culture of collaboration and efficiency. Here are some prevalent myths surrounding delegation:
- Delegation is a Sign of Weakness: Many believe that asking others for help indicates a lack of capability or leadership strength. In reality, effective delegation is a hallmark of strong leadership.
- Only Managers Can Delegate: While managers often delegate tasks, anyone can and should delegate responsibilities within their capacity. It encourages teamwork and growth among peers.
- Delegation Means Abdication: Some people think that delegating a task means relinquishing all responsibility. However, effective delegation includes maintaining accountability while empowering others.
- All Tasks Can Be Delegated: Not every task is suitable for delegation. Understanding which tasks to delegate and which to retain is essential for effective time management.
“Effective delegation is not about passing off tasks; it is about enabling others to grow while enhancing overall productivity.”
Identifying Tasks to Delegate
Identifying tasks suitable for delegation is a crucial step in freeing up your time and optimizing team performance. By systematically categorizing tasks, you can focus on what truly requires your attention while empowering your team members to take on additional responsibilities.One effective method for categorizing tasks involves using the Eisenhower Matrix, a tool developed by former U.S. President Dwight D.
Eisenhower. This matrix helps in distinguishing tasks based on their urgency and importance. Tasks are divided into four quadrants:
1. Urgent and Important
These tasks require immediate attention and must be done by you.
2. Important but Not Urgent
These tasks are significant for long-term goals but can be scheduled for later. They are ideal candidates for delegation.
3. Urgent but Not Important
Tasks that demand immediate attention but do not significantly impact your goals can be delegated to others.
4. Not Urgent and Not Important
These tasks can often be eliminated or delegated to others with minimal impact on overall productivity.
Commonly Suitable Tasks for Delegation
In various work environments, certain tasks are universally recognized as suitable for delegation. Understanding these tasks can help streamline operations and enhance productivity. The following list Artikels tasks that are commonly delegated:
- Administrative duties such as scheduling meetings, data entry, and filing documents.
- Customer service inquiries that can be addressed by support staff.
- Research tasks where team members can gather information on specific topics.
- Project management tasks, including monitoring progress and updating stakeholders.
- Routine reporting and analysis of data that does not require your direct oversight.
The importance of recognizing these tasks lies in their ability to free up your time for strategic planning and decision-making, ultimately enhancing overall productivity.
Assessing Team Members’ Strengths for Task Matching
To delegate effectively, it is essential to assess your team members’ strengths and skills. This ensures that tasks are matched with individuals who possess the appropriate competencies to execute them successfully. Begin by conducting a skills inventory or assessment to understand each team member’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas of expertise. Consider the following aspects:
- Professional experience and qualifications that align with specific tasks.
- Previous performance on similar tasks, highlighting their ability to deliver results.
- Interest and enthusiasm for particular assignments, which can enhance motivation.
- Availability and workload capacity to ensure delegation does not overwhelm them.
By considering these factors, you can assign tasks that not only utilize your team members’ strengths but also foster their professional growth and job satisfaction.
Effective delegation is not just about offloading tasks; it is about strategically assigning responsibilities to enhance team capabilities and drive success.
Choosing the Right People for Delegation

Selecting the appropriate team members for delegated tasks is a critical factor in the success of delegation. Ensuring that the right individuals are entrusted with specific responsibilities not only enhances productivity but also fosters a sense of ownership among team members. This section delves into effective strategies for identifying the best candidates for delegation, the significance of trust in this process, and an action plan to develop the skills of team members for their new roles.
Strategies for Selecting Team Members
Identifying the right individuals for delegated tasks requires a strategic approach. Here are some methodologies to consider:
- Assess Skills and Strengths: Evaluate team members’ skills, strengths, and past performance. Understanding their areas of expertise allows for better alignment between the task and the individual’s capabilities.
- Consider Interest and Motivation: Engage with team members to gauge their interest in taking on new responsibilities. Individuals who are motivated and enthusiastic are more likely to succeed in their tasks.
- Evaluate Workload: Review current workloads to ensure that the individuals selected have the capacity to take on additional tasks without compromising their existing responsibilities.
Importance of Trust in Delegation
Trust plays a pivotal role in the delegation process. A strong foundation of trust enables effective communication and collaboration, fostering a positive environment for both leaders and team members. Building trust can be achieved through the following methods:
- Open Communication: Foster an environment where team members feel comfortable expressing their thoughts, concerns, and feedback. This transparency builds mutual respect.
- Consistency: Consistently follow through on commitments and support team members, reinforcing the reliability of leadership.
- Empowerment: Encourage autonomy and empower team members to make decisions related to their tasks. This not only builds confidence but also strengthens trust in their abilities.
Action Plan for Skill Development
Preparing team members for new responsibilities through skill development is essential for effective delegation. Implementing a structured action plan can facilitate this growth as Artikeld below:
- Identify Skill Gaps: Conduct assessments to identify specific skills that need development. This can be done through performance reviews or informal feedback sessions.
- Provide Training Opportunities: Organize training programs, workshops, and online courses tailored to the identified skill gaps. Encourage team members to participate actively.
- Assign Mentorship: Pair less experienced team members with mentors who can provide guidance and support. This relationship can enhance learning and foster confidence.
- Set Clear Objectives: Establish measurable goals for each team member as they take on new responsibilities. Regularly review progress and provide constructive feedback.
“Effective delegation is not just about assigning tasks; it’s about building a strong team that can thrive under responsibility.”
Communicating Effectively During Delegation
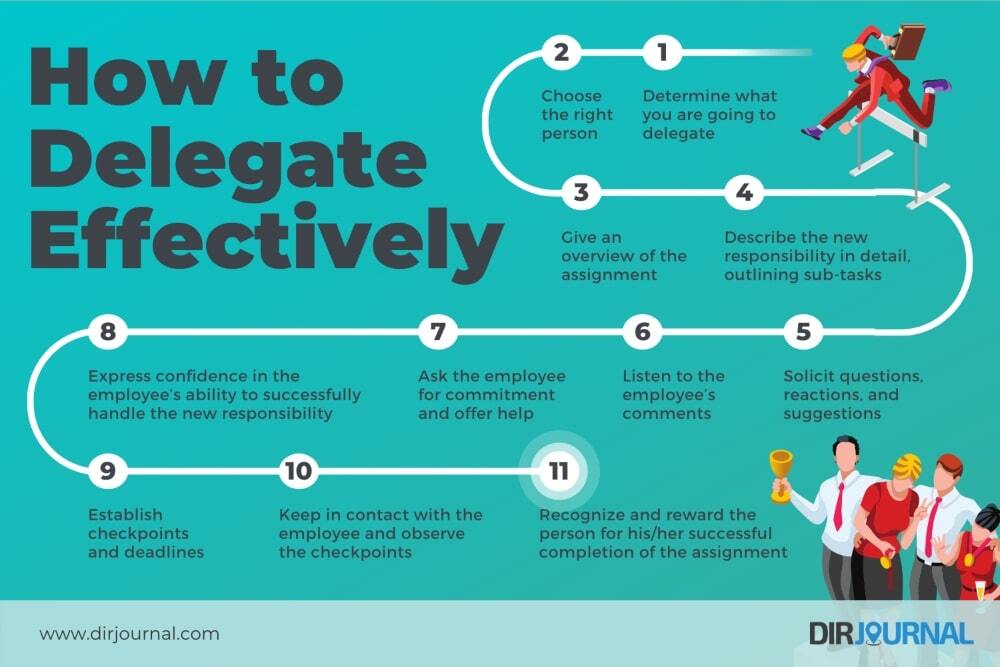
Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful task delegation. Articulating expectations clearly not only ensures that your delegatee understands their responsibilities but also fosters a collaborative atmosphere where feedback is valued. By implementing structured communication strategies, you can enhance the delegation process, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and to the desired standard.
Articulating Expectations Clearly
To delegate tasks successfully, it is crucial to articulate expectations with precision. This involves not only outlining the specific tasks but also detailing the desired outcomes and any relevant deadlines. Clear articulation minimizes misunderstandings and sets the stage for accountability.
“Clarity breeds confidence; when expectations are clearly defined, the delegatee can execute tasks with assurance.”
When communicating expectations, consider the following elements:
- Specificity: Define the task with clear, specific details. For example, instead of saying, “Prepare a report,” specify, “Prepare a market analysis report by Friday, including data on recent trends and competitor analysis.”
- Outcomes: Describe what success looks like. For instance, “The report should provide actionable insights that can guide our marketing strategy.”
- Deadlines: Set clear timelines. Ensure the delegatee understands not only when the task is due but also any critical milestones along the way.
- Resources: Inform the delegatee about available resources and tools that can assist them in completing the task.
Providing Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback is vital throughout the delegation process. It serves not only to guide the delegatee but also to reinforce their confidence and competence. Feedback should be timely, specific, and focused on behaviors rather than personal attributes.
“Feedback is a gift; providing it effectively can enhance performance and foster growth.”
Effective methods for giving feedback include:
- Regular Check-ins: Schedule periodic meetings to discuss progress and provide feedback. This can help address any issues before they escalate.
- Positive Reinforcement: Acknowledge and commend good work. Recognizing achievements motivates the delegatee and encourages continued effort.
- Constructive Criticism: When addressing areas for improvement, be specific about the behavior that needs adjustment and suggest actionable steps for improvement.
- Open Dialogue: Foster an environment where the delegatee feels comfortable sharing their thoughts and asking questions. This openness facilitates better understanding and teamwork.
Checklist for Conveying Necessary Information
A comprehensive checklist can ensure that all necessary information is conveyed to the delegatee. This minimizes the risk of miscommunication and enhances clarity.
“A well-structured checklist is instrumental in facilitating effective delegation and ensuring nothing is overlooked.”
The checklist should include:
- Task description and objectives
- Specific outcomes expected
- Deadlines and key milestones
- Available resources and tools
- Point of contact for questions or clarification
- Feedback mechanisms and timelines for evaluation
Monitoring Progress and Providing Support
Monitoring progress is a crucial aspect of delegation that ensures tasks are completed effectively while also providing a support system for those to whom tasks have been delegated. Setting up a structured approach for regular check-ins fosters accountability and aids in uncovering any challenges the team may face. It also reinforces a collaborative environment where team members feel supported and valued.Establishing regular check-ins can help maintain clarity regarding the status of delegated tasks.
These meetings should be scheduled at intervals that suit both the complexity of the task and the team’s workflow, thereby allowing for timely feedback and adjustments. Routine updates not only help in tracking progress but can also serve as a motivational tool for team members.
Setting Up Regular Check-Ins
Implementing a schedule for regular check-ins is essential for effective task management. Here are some key points to consider when establishing these meetings:
- Frequency: Determine the frequency of check-ins based on the complexity of the tasks. Weekly or bi-weekly meetings are generally effective for ongoing projects.
- Format: Decide on the format of the check-ins, whether they will be one-on-one meetings or team huddles, to facilitate open communication.
- Duration: Keep the check-ins brief and focused, ideally lasting no longer than 30 minutes to respect everyone’s time.
- Agenda: Prepare an agenda for each meeting, specifying what topics will be discussed, such as progress updates, challenges faced, and next steps.
Utilizing these strategies promotes an environment where team members feel encouraged to share their progress and obstacles without fear of undue criticism.
Offering Support Without Micromanaging
While monitoring progress is important, offering support should not devolve into micromanagement. Encouraging autonomy while still providing assistance can be achieved through several techniques:
- Empowerment: Encourage team members to make decisions related to their tasks, fostering a sense of ownership.
- Open-Door Policy: Maintain availability for questions or guidance without hovering over their shoulders, promoting open communication.
- Feedback Mechanism: Foster a culture of constructive feedback where team members can share concerns and suggestions without feeling judged.
By striking the right balance, leaders can ensure that their support empowers rather than stifles the team’s capabilities.
Progress Reporting Template
Creating a progress reporting template encourages accountability among team members while facilitating efficient communication. A structured format can guide individuals in providing relevant updates and identifying areas needing attention. Below is an example of a straightforward template for progress reporting:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Task Name | Specify the name of the task being reported on. |
| Current Status | Provide a brief summary of the progress made (e.g., Not Started, In Progress, Completed). |
| Accomplishments | Highlight notable achievements or milestones reached since the last report. |
| Challenges | Identify any issues or obstacles encountered that may hinder progress. |
| Next Steps | Artikel the upcoming actions to be taken or decisions needed. |
By utilizing this template, team members can provide clear, concise updates that not only emphasize their accountability but also facilitate problem-solving discussions during check-ins.
Evaluating Outcomes and Learning from the Experience

Evaluating the results of delegated tasks is essential to understanding their impact on both individual and team productivity. By analyzing outcomes, you can identify areas for improvement and guide future delegation efforts. This process not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to the development of team members.
Key Performance Indicators for Measuring Success
Establishing clear key performance indicators (KPIs) is vital in assessing the success of delegated tasks. These indicators provide measurable insights into the effectiveness and outcomes of the delegation process. Common KPIs include:
- Completion Rate: The percentage of tasks completed on time compared to those assigned.
- Quality of Work: Evaluation based on predefined standards or feedback from peers and stakeholders.
- Employee Engagement: Monitoring team members’ satisfaction and involvement in the delegated tasks through surveys or one-on-one discussions.
- Time Management: Assessing whether tasks were completed within the expected timeframe and identifying any delays.
- Contribution to Goals: Measuring the extent to which the completed tasks align with broader organizational objectives.
Conducting a Post-Task Review with the Team
A post-task review is a structured discussion aimed at evaluating the outcomes of delegated tasks. This review provides an opportunity for team members to reflect on their experiences, share insights, and learn from each other. Important elements to consider during the review include:
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from team members regarding challenges faced and successes achieved during the task.
- Performance Analysis: Compare actual outcomes against the established KPIs to assess effectiveness.
- Identification of Improvement Areas: Discuss what could be improved in terms of delegation strategies, resources provided, and communication methods.
- Documentation of Lessons Learned: Record key insights and suggestions for future delegation efforts to create a repository of best practices.
Importance of Celebrating Successes and Addressing Failures
Recognizing both successes and failures is crucial in the delegation process. Celebrating successes not only boosts morale but also reinforces positive behaviors and encourages continued high performance. Conversely, addressing failures provides a learning opportunity that can lead to significant improvements in future delegations.
“Celebrating small wins creates a culture of appreciation and motivation within the team.”
When addressing failures, it is essential to approach the discussion constructively. This involves:
- Open Dialogue: Encourage candid conversations about what went wrong and how to rectify it.
- Solution-Focused Approach: Emphasize what can be learned rather than placing blame, fostering a growth mindset within the team.
- Adjusting Strategies: Use insights gained from failures to adapt delegation strategies, ensuring better alignment with team capabilities in the future.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, mastering the art of delegation is a powerful way to enhance both personal and team productivity. By understanding the principles of effective delegation, identifying appropriate tasks, and selecting the right individuals, you can ensure that your team thrives while you free up valuable time for strategic initiatives. Always remember to monitor progress and provide constructive feedback, as these practices lead to continuous improvement and success.
As you reflect on your delegation experiences, celebrate the achievements and learn from the challenges, paving the way for a more efficient and harmonious work environment.